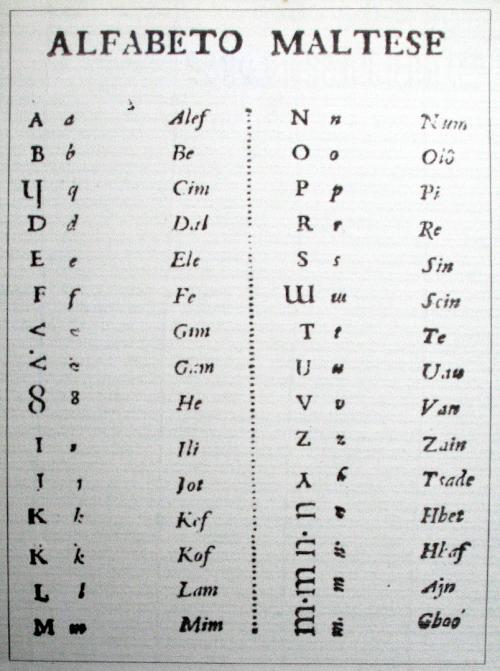
Learning the Malta language can open doors to a rich cultural experience and enhance communication with locals during your visit to this stunning Mediterranean island. Malta, a small yet vibrant country, boasts a unique linguistic heritage that combines elements of Semitic, Romance, and Germanic languages. Understanding the nuances of the Maltese language can significantly enrich your travel experience and foster meaningful connections with the people of Malta.
Malta's official languages are Maltese and English, with Maltese being the national language. The Maltese language, known for its distinct sounds and vocabulary, has deep historical roots that reflect the country's diverse influences. This article will provide an in-depth exploration of the Maltese language, its origins, structure, and practical tips for learning it.
Whether you're planning a trip to Malta or simply interested in expanding your linguistic knowledge, this guide will equip you with the essential tools to understand and appreciate the Malta language. Let's dive into the fascinating world of Maltese linguistics and discover what makes it so unique.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Disney World Theme Park Tickets
Table of Contents
- The Rich History of Malta Language
- Understanding the Structure of Maltese Language
- Mastering Maltese Pronunciation
- Exploring Maltese Vocabulary
- Key Features of Maltese Grammar
- Effective Strategies for Learning Malta Language
- Top Resources for Malta Language Learners
- Practical Tips for Speaking Maltese
- Cultural Insights into Malta Language
- Conclusion: Embrace the Malta Language Journey
The Rich History of Malta Language
The Malta language, officially known as Maltese, has a fascinating history that dates back centuries. It is the only Semitic language written in the Latin alphabet and reflects a blend of influences from various civilizations that have inhabited the Maltese islands. The origins of the Maltese language can be traced to the Siculo-Arabic dialect spoken in Sicily and Malta during the Arab domination of the region from the 9th to the 13th centuries.
Over time, the Maltese language evolved through interactions with Italian, French, and English, resulting in a unique linguistic identity. Today, Maltese is spoken by approximately 520,000 people, primarily in Malta, but also in diaspora communities around the world. Its historical significance is underscored by its status as an official language of the European Union.
Historical Influences on Maltese Language
- Arabic Influence: The foundation of Maltese vocabulary and grammar is rooted in Arabic, particularly in its root-and-pattern morphology.
- Italian Influence: Italian loanwords account for a significant portion of modern Maltese vocabulary, especially in formal contexts.
- English Influence: Due to British colonial rule, English has contributed numerous loanwords and technical terms to the Maltese lexicon.
Understanding the Structure of Maltese Language
To effectively learn the Malta language, it's crucial to understand its structural components. Maltese is characterized by its unique grammar, syntax, and vocabulary. One of the most distinctive features of the Maltese language is its triconsonantal root system, where words are built around a core set of consonants with varying vowel patterns.
Maltese also employs a rich system of verb conjugation and noun declension, influenced by both Semitic and Romance linguistic traditions. This complexity adds depth to the language but can pose challenges for learners unfamiliar with these structures.
Key Structural Features of Maltese Language
- Triconsonantal Roots: Maltese words are formed using a system of three-consonant roots, which serve as the basis for verbs, nouns, and adjectives.
- Verb Conjugation: Verbs in Maltese are conjugated based on tense, mood, voice, and person, similar to Romance languages.
- Noun Declension: Nouns in Maltese change form to indicate case, number, and gender, reflecting its Semitic origins.
Mastering Maltese Pronunciation
Pronunciation is a critical aspect of learning any language, and Maltese is no exception. The Malta language features several unique sounds that may be unfamiliar to English speakers. For instance, Maltese includes emphatic consonants, such as "ħ" (similar to the "ch" in Scottish "loch") and "q" (a glottal stop). These sounds require practice to master but are essential for clear communication in Maltese.
Additionally, Maltese vowels are pronounced distinctly, with long and short forms that can alter the meaning of words. Paying attention to vowel length and stress patterns will greatly improve your ability to pronounce Maltese words accurately.
Read also:How To Create Viral Mms For Social Media Marketing The Ultimate Guide
Tips for Improving Maltese Pronunciation
- Listen to native speakers through podcasts, videos, or language exchange platforms.
- Practice tongue twisters and repetitive exercises to refine your pronunciation.
- Use phonetic guides and audio resources to ensure correct articulation of sounds.
Exploring Maltese Vocabulary
Building a robust vocabulary is essential for fluency in the Malta language. Maltese vocabulary draws from a variety of sources, including Arabic, Italian, and English. This linguistic diversity makes Maltese both challenging and rewarding to learn. Common Maltese words and phrases often reflect the country's cultural heritage and daily life.
For example, basic greetings in Maltese include "Għadda'" (hello) and "Saħħa" (good health). Understanding everyday vocabulary will enhance your ability to communicate effectively with locals and immerse yourself in Maltese culture.
Common Maltese Words and Phrases
- Għadda' - Hello
- Saħħa - Good health
- Jekk jogħġbok - Please
- Ġrazzi - Thank you
Key Features of Maltese Grammar
Maltese grammar is complex yet logical, combining elements from Semitic and Romance linguistic traditions. One of the most distinctive features of Maltese grammar is its use of verbal conjugation to indicate tense, mood, and voice. Verbs in Maltese are typically constructed around a triconsonantal root, with vowel patterns and affixes modifying their meaning and function.
Nouns in Maltese are gendered, with masculine and feminine forms, and decline according to case, number, and definiteness. Understanding these grammatical rules is crucial for constructing coherent sentences in the Malta language.
Understanding Maltese Verb Conjugation
- Present Tense: Verbs in the present tense are conjugated based on person and number.
- Past Tense: The past tense in Maltese is formed by adding prefixes and suffixes to the root verb.
- Future Tense: Future tense is indicated by using the auxiliary verb "jista'" followed by the infinitive form of the main verb.
Effective Strategies for Learning Malta Language
Learning the Malta language requires dedication and a structured approach. Effective strategies for mastering Maltese include consistent practice, immersion, and the use of diverse learning resources. Setting clear goals and tracking progress can also motivate learners to stay committed to their language journey.
Engaging with native speakers through language exchange programs or travel to Malta can accelerate learning and improve fluency. Additionally, leveraging technology such as language learning apps and online courses can provide flexible and accessible learning opportunities.
Recommended Learning Resources
- Language Learning Apps: Duolingo, Babbel, and Memrise offer Maltese courses for beginners and intermediate learners.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Udemy and Coursera provide comprehensive Maltese language courses taught by experienced instructors.
- Podcasts and YouTube Channels: Listening to Maltese podcasts and watching videos in the language can improve listening skills and comprehension.
Top Resources for Malta Language Learners
Access to quality resources is essential for successful language learning. The Malta language has a growing number of resources available for learners, ranging from textbooks and dictionaries to multimedia content. Utilizing a combination of traditional and digital resources can enhance the learning experience and cater to different learning styles.
For beginners, starting with a Maltese-English dictionary and a grammar guide can provide a solid foundation. Intermediate and advanced learners can explore literature, news articles, and cultural materials in Maltese to deepen their understanding of the language.
Essential Maltese Language Resources
- Maltese-English Dictionary: A comprehensive dictionary for vocabulary building.
- Grammar Guides: Detailed guides explaining Maltese grammar rules and structures.
- Cultural Materials: Books, films, and music in Maltese to immerse learners in the language.
Practical Tips for Speaking Maltese
Practicing speaking is one of the most effective ways to improve fluency in the Malta language. Engaging in conversations with native speakers, participating in language exchange programs, and practicing regularly can significantly enhance speaking skills. Overcoming fear of making mistakes is key to becoming a confident Maltese speaker.
Additionally, recording oneself speaking Maltese and seeking feedback from native speakers can help identify areas for improvement. Consistent practice and exposure to the language will gradually build confidence and fluency in speaking Maltese.
Speaking Practice Techniques
- Language Exchange Programs: Connect with native Maltese speakers for mutual language learning.
- Speaking Groups: Join local or online groups dedicated to practicing Maltese conversation.
- Self-Recording: Record yourself speaking Maltese to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Cultural Insights into Malta Language
Language and culture are deeply intertwined, and understanding the cultural context of the Malta language can enhance the learning experience. Maltese culture is rich in traditions, festivals, and customs that reflect the country's diverse history and influences. Language plays a central role in preserving and celebrating these cultural aspects.
For example, traditional Maltese festivals such as "Il-Festa" incorporate elements of language, music, and dance that showcase the country's cultural heritage. Engaging with these cultural practices can provide valuable insights into the Maltese language and its significance in daily life.
Cultural Events and Language
- Il-Festa: A vibrant celebration of saints and local traditions, featuring Maltese music and language.
- Malti Literature: Exploring Maltese literature offers a deeper understanding of the language and its cultural context.
- Traditional Songs: Listening to Maltese folk songs can improve comprehension and appreciation of the language.
Conclusion: Embrace the Malta Language Journey
In conclusion, learning the Malta language offers a rewarding opportunity to connect with a rich cultural heritage and enhance communication with locals during your visit to Malta. This comprehensive guide has explored the history, structure, vocabulary, and grammar of the Maltese language, providing practical tips and resources for learners at all levels.
We encourage you to take the first step in your Malta language journey by practicing regularly, engaging with native speakers, and immersing yourself in the cultural context of the language. Share your experiences and insights in the comments below, and explore other articles on our site for further language learning inspiration.