When it comes to determining the hottest state in the United States, several factors come into play, including average temperature, climate patterns, and geographic location. The United States spans a wide range of climates, from the icy tundras of Alaska to the scorching deserts of the Southwest. However, one state stands out for its relentless heat and consistently high temperatures. Understanding which state is the hottest not only satisfies curiosity but also provides valuable insights into climate science, geography, and environmental adaptation.
The topic of the hottest state in the U.S. is not just a matter of trivia. It has significant implications for public health, energy consumption, agriculture, and urban planning. As global temperatures continue to rise due to climate change, understanding which areas are most affected by extreme heat becomes increasingly important. This article will delve into the details, providing comprehensive information backed by scientific data and expert analysis.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of which state holds the title of the hottest in the nation, why it earns this distinction, and what it means for its residents and visitors. Whether you're planning a trip, studying climate patterns, or simply curious about geography, this guide will provide the answers you seek.
Read also:Resultados Presidenciales 2024 Todo Lo Que Necesitas Saber
Table of Contents
- Overview of the Hottest State in the U.S.
- Factors Contributing to Extreme Heat
- Arizona: The Hottest State
- Temperature Data and Statistics
- Impact of Extreme Heat on Daily Life
- Other Hot States in the U.S.
- Health Risks Associated with Extreme Heat
- Strategies for Adapting to Heat
- The Role of Climate Change
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Overview of the Hottest State in the U.S.
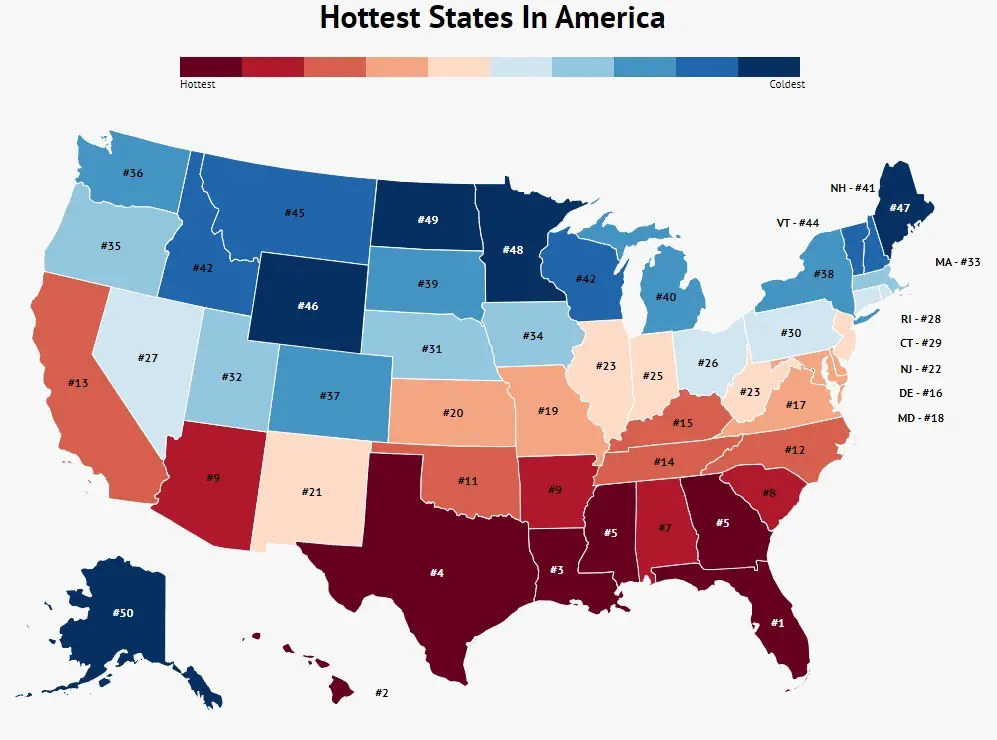
When discussing the hottest state in the United States, Arizona often takes center stage. This southwestern state is renowned for its desert landscapes, arid climate, and consistently high temperatures. While other states may experience hot weather during certain seasons, Arizona's year-round heat makes it the clear winner in this category. The state's location within the Sonoran Desert contributes significantly to its extreme temperatures.
The combination of low humidity, clear skies, and intense solar radiation creates an environment where temperatures can soar above 100°F (38°C) for extended periods. Cities like Phoenix and Tucson, two of Arizona's largest metropolitan areas, regularly experience record-breaking heatwaves. This overview sets the stage for a deeper exploration of why Arizona earns the title of the hottest state in the nation.
Factors Contributing to Extreme Heat
Geographic Location and Topography
Arizona's geographic location plays a crucial role in its extreme heat. Situated in the southwestern United States, the state is dominated by desert landscapes and mountain ranges. The Sonoran Desert, which covers much of southern Arizona, is one of the hottest deserts in North America. Its low elevation and sparse vegetation contribute to the region's high temperatures.
Additionally, the state's topography creates a "heat island" effect in urban areas like Phoenix. Concrete structures and asphalt roads absorb and retain heat, raising temperatures even further. This phenomenon is exacerbated by the lack of natural cooling mechanisms, such as water bodies or dense forests.
Climate Patterns and Weather Systems
Arizona's climate is characterized by its arid conditions and distinct seasonal variations. Summers are marked by intense heat, with temperatures often exceeding 110°F (43°C) in the desert regions. Monsoon season, which typically occurs from July to September, brings brief but intense thunderstorms that provide temporary relief from the heat. However, the moisture in the air during this period can make the heat feel even more oppressive.
In contrast, winters in Arizona are relatively mild, with temperatures averaging in the 50s and 60s°F (10-20°C). This seasonal variation highlights the state's unique climate, where extreme heat is a defining feature.
Read also:Keith Sutherland A Deep Dive Into The Life Of A Versatile Actor
Arizona: The Hottest State
Arizona's reputation as the hottest state in the U.S. is well-deserved. Its capital city, Phoenix, holds the record for the highest number of days per year with temperatures above 100°F. In fact, Phoenix averages over 100 such days annually, with some years surpassing 130 days. The state's largest city serves as a microcosm of the challenges and adaptations associated with extreme heat.
Tucson, another major city in Arizona, also experiences scorching temperatures, albeit slightly cooler than Phoenix due to its higher elevation. Both cities have developed strategies to cope with the heat, including investing in cooling infrastructure, promoting water conservation, and educating residents about heat safety.
Temperature Data and Statistics
Historical Temperature Records
Arizona has been the site of some of the highest recorded temperatures in the United States. On June 29, 1994, the city of Lake Havasu recorded a blistering 128°F (53°C), one of the hottest temperatures ever measured in the nation. While this record is not officially recognized as the highest, it underscores the extreme heat conditions that Arizona regularly experiences.
According to data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Arizona's average high temperature has steadily increased over the past few decades. This trend aligns with broader patterns of global warming, highlighting the state's vulnerability to climate change.
Comparative Analysis with Other States
While Arizona is widely regarded as the hottest state, other states in the Southwest also experience significant heat. California, Nevada, and New Mexico frequently rank among the hottest states due to their desert climates. However, Arizona's combination of high temperatures, low humidity, and prolonged heatwaves sets it apart from its neighbors.
Data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) shows that Arizona has the highest number of heat-related deaths per capita among all states. This statistic underscores the serious public health implications of extreme heat and the need for effective mitigation strategies.
Impact of Extreme Heat on Daily Life
Urban Planning and Infrastructure
Extreme heat has a profound impact on urban planning and infrastructure in Arizona. Cities like Phoenix and Tucson have implemented measures to combat the urban heat island effect, including planting trees, using reflective roofing materials, and designing public spaces with shade in mind. These efforts aim to create more livable environments for residents and visitors alike.
Transportation systems in Arizona are also adapted to withstand high temperatures. Roads and highways are constructed with heat-resistant materials, and public transit systems incorporate cooling features such as air-conditioned buses and shaded stations.
Public Health and Safety
Heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion and heat stroke, are significant public health concerns in Arizona. The state's public health department actively promotes awareness campaigns to educate residents about the dangers of extreme heat and how to stay safe. Measures such as staying hydrated, avoiding outdoor activities during peak heat hours, and seeking shelter in air-conditioned spaces are emphasized.
Emergency services in Arizona are well-prepared to handle heat-related emergencies, with specialized training and equipment to address the unique challenges posed by extreme temperatures.
Other Hot States in the U.S.
California: A Close Contender
California, with its diverse climate zones, is another state known for its hot weather. The Mojave Desert, which spans parts of California, Nevada, and Arizona, is one of the driest and hottest regions in the world. Death Valley, located in California, holds the record for the highest air temperature ever recorded on Earth at 134°F (56.7°C).
Despite its reputation for heat, California's coastal regions provide a cooler alternative, thanks to the moderating influence of the Pacific Ocean. This contrast highlights the state's varied climate and its ability to support a wide range of ecosystems.
Nevada: A Desert State
Nevada, like Arizona, is dominated by desert landscapes and experiences extreme heat during the summer months. Las Vegas, the state's largest city, frequently records temperatures above 110°F (43°C). However, Nevada's smaller population and less dense urban areas result in fewer heat-related challenges compared to Arizona.
The state's efforts to combat heat include promoting energy-efficient building practices and encouraging the use of renewable energy sources such as solar power.
Health Risks Associated with Extreme Heat
Extreme heat poses significant health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. Heat-related illnesses can range from mild symptoms like heat cramps to life-threatening conditions such as heat stroke. Dehydration, sunburn, and respiratory issues are also common consequences of prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Public health experts recommend taking preventive measures to mitigate these risks. Staying hydrated, wearing protective clothing, and limiting outdoor activities during peak heat hours are essential strategies for staying safe in hot weather.
Strategies for Adapting to Heat
Technological Innovations
Advances in technology have provided new tools for adapting to extreme heat. Smart thermostats, energy-efficient appliances, and advanced cooling systems are just a few examples of innovations that help residents stay comfortable in hot climates. Solar-powered solutions, such as air conditioning units and water heaters, offer sustainable alternatives to traditional energy sources.
Urban planners are also exploring the use of green infrastructure, such as green roofs and vertical gardens, to reduce heat absorption and improve air quality in urban areas.
Community Initiatives
Community-based initiatives play a vital role in addressing the challenges of extreme heat. Programs that provide access to cooling centers, distribute water and sunscreen, and offer educational resources help ensure that all residents, regardless of socioeconomic status, can stay safe during heatwaves. Collaboration between government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private sector partners is essential for the success of these initiatives.
The Role of Climate Change
Climate change is a key factor driving the increase in extreme heat across the United States, including in Arizona. Rising greenhouse gas emissions trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to higher average temperatures and more frequent heatwaves. This trend is expected to continue, with projections indicating that Arizona and other southwestern states will experience even hotter conditions in the coming decades.
Tackling climate change requires a global effort, but local actions can also make a significant difference. Reducing carbon emissions, investing in renewable energy, and promoting sustainable practices are crucial steps toward mitigating the impacts of extreme heat and ensuring a livable future for all.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Arizona stands out as the hottest state in the United States due to its unique combination of geographic, climatic, and environmental factors. The state's extreme heat presents both challenges and opportunities, requiring innovative solutions and collaborative efforts to address its impacts. By understanding the causes and consequences of extreme heat, we can better prepare for the future and protect the health and well-being of communities across the nation.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Have you visited Arizona or other hot states in the U.S.? What strategies do you use to stay cool in extreme heat? For more informative articles on geography, climate, and environmental science, explore our other content and stay connected with our latest updates.